Compared to variable costing, absorption costing income statements tend to show less volatility in operating income from period to period. This is because fixed costs are smoothed into COGS rather than impacting the period they are incurred. Fixed manufacturing overhead costs are indirect costs and they are absorbed based on the cost driver.
Objectives of Absorption Costing
Absorption costing is linking all production costs to the cost unit to calculate a full cost per unit of inventories. This costing method treats all production costs as costs of the product regardless of fixed cost or variance cost. It is sometimes called the full costing method because it includes all costs to get a cost unit. Those costs include direct costs, variable overhead costs, and fixed overhead costs. Absorption costing and variable costing are two different methods of costing that are used to calculate the cost of a product or service.
Table of Contents
Variable costing will result in a lower breakeven price per unit using COGS. This can make it somewhat more difficult to determine the ideal pricing for a product. Variable costing results in gross profit that will be slightly higher, resulting in a slightly higher gross profit margin compared to absorption costing.
Please Sign in to set this content as a favorite.
- The prime cost, comprising direct materials, direct labor, and direct expenses, is significant in every type of organization.
- This cost includes direct production costs like materials and wages as well as a share of fixed costs allocated to each unit.
- Many accountants claim that administrative, fixed manufacturing, and marketing and distribution overheads are period costs.
- Most companies may have to transition to absorption costing at some point, however, and it can be important to factor this into short-term and long-term decision-making.
This content is for general information purposes only, and should not be used as a substitute for consultation with professional advisors. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be how can i change the language setting to spanish investment or tax advice. All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. This is one of the oldest methods of cost absorption and it is widely regarded as one of the best.
Absorption Costing Calculation
Once the cost pools have been determined, the company can calculate the amount of usage based on activity measures. This usage measure can be divided into the cost pools, creating a cost rate per unit of activity. Usually, the amount of the overheads and the value of direct materials are determined from past experience, and the overhead rate is calculated in advance. The overhead rate can be determined by dividing the total estimated overheads of the cost center or job by the total estimated units of output. It refers to the application of overheads based on the number of units of output manufactured during the period. Using these methods, overheads are recovered, charged to, or absorbed in the factory cost.
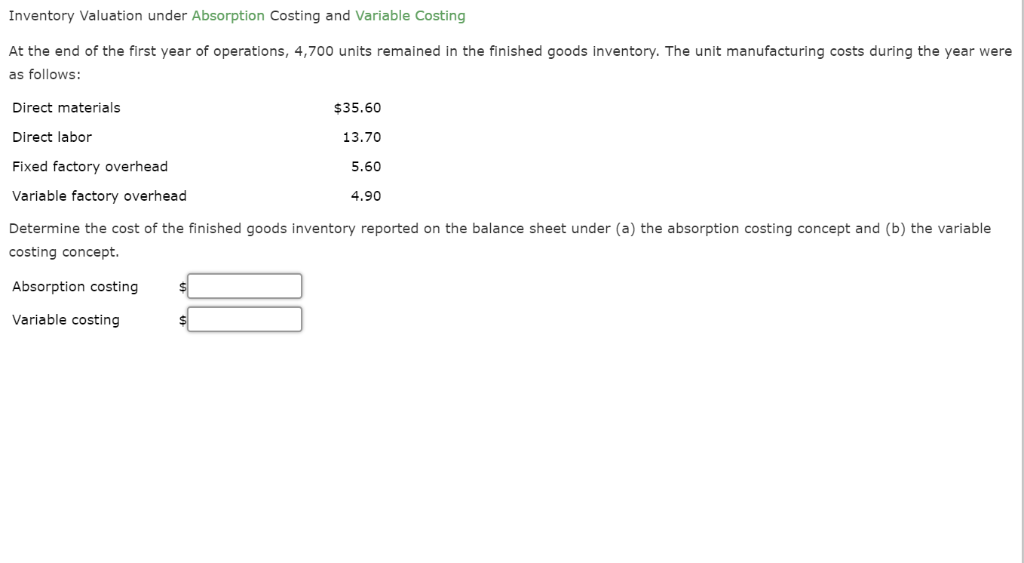
Variable costs can be more valuable for short-term decision-making, giving a guide to operating profit if there’s a bump-up in production to meet holiday demand, for example. Depending on a company’s level of transparency, an income statement using absorption costing may break variable direct costs and fixed direct costs into two line items or combine them to report a comprehensive COGS. The variable direct costs and fixed direct costs are subtracted from revenue to arrive at the gross profit in either case. This cost includes direct production costs like materials and wages as well as a share of fixed costs allocated to each unit.
A company may also be required to use the absorption costing method for reporting purposes if it prefers the variable costing method for management decision-making purposes. Overall, absorption costing adheres to GAAP principles for inventory valuation and provides a full allocation of all manufacturing costs to inventory and cost of goods sold. But the inventory values and net income figures can vary significantly between periods as inventory levels and production volumes fluctuate. It is possible to use activity-based costing (ABC) to allocate overhead costs for inventory valuation purposes under the absorption costing methodology. However, ABC is a time-consuming and expensive system to implement and maintain, and so is not very cost-effective when all you want to do is allocate costs to be in accordance with GAAP or IFRS. Additionally, it is not helpful for analysis designed to improve operational and financial efficiency or for comparing product lines.
The prime cost, comprising direct materials, direct labor, and direct expenses, is significant in every type of organization. The percentage of direct labor cost method of overhead absorption is also useful due to the simple fact that the labor rate, as compared to other rates in the elements of cost, is more stable. Thus, the absorption of overheads is the function of apportioning overhead costs to individual units, jobs, production lots, processes, work-orders, or such other convenient cost units. A company must pay its manufacturing property mortgage payments every month regardless of whether it produces 1,000 products or no products at all. It may see an increase in gross profit after paying off the mortgage or finishing the depreciation schedule on a piece of manufacturing equipment. These are considerations that cost accountants must closely manage when using absorption costing.